6.4 数据校验 6.4.2 JSR 303校验 JSR 303是Java为Bean数据合法性校验所提供的一个标准规范,叫作Bean Validation。2009年12月Java EE6发布,Bean Validation 作为一个重要特性被包含其中,用于对JavaBean中的字段值进行验证 。官方参考实现是Hibernate Validation。Bean Validation为 JavaBean验证定义了相应的元数据类型和API。在应用程序中通过在Bean属性上标注类似于@NotNull、@Max等标准的注解指定校验规则,并通过标注的验证接口对Bean进行验证。Bean Validation是一个运行时的数据验证框架,在验证之后验证的错误信息会被马上返回。http://jcp.org/en/jsr/detail?id=303 了解JSR 303的详细内容。JSR 303是一个规范,它的核心接口是Javax.validation.Validator ,该接口根据目标对象类中所标注的校验注解进行数据校验,并得到校验结果。
下载JSR 303 JSR 303目前有两个实现第一个实现是 Hibernate Validator,可以从以下网站下载:https://sourceforge.net/projects/hibernate/files/hibernate-validator/ Apache bval,可以从以下网站下载:http://bval.apache.org/downloads.html
JSR 303注解 JSR 303中定义了一套可标注在成员变量、属性方法上的校验注解
注解
功能
范例
@Null验证对象是否为null
@Null
@NotNull验证对象是否不为null,无法检查长度为0的字符串,用于验证基本数据类型
@NotNull
@NotBlank检查约束字符串是不是null,被Trim的长度是否大于0,只作用于字符串,且会去掉前后空格
@NotBlank
@AssertTrue验证Boolean对象是否为true
@AssertTrue
@AssertFalse验证Boolean对象是否为false
@AssertTrue
@Max(value)验证Number和String对象是否小于或者等于 指定的值
@Max(0)
@Min(value)验证Number和String对象是否大于或者等于 指定的值
@Min(160)
@DecimalMax(value)被标注的值必须不大于约束中指定的最大值 .。这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最大值的字符串表示,小数存在精度
@DecimalMax(1.1)
@DecimalMin(value)被标注的值必须不小于约束中指定的最小值 .。这个约束的参数是一个通过BigDecimal定义的最小值的字符串表小数存在精度
@DecimalMax(0.5)
@Digits(integer,fraction)验证字符串是否是符合指定格式的数字 ,Integer指定整数精度,fraction指定小数精度
@Digits(integer=5, fraction=2)
@Size(min,max)验证对象(Array、Collection、Map、String)长度是否在给定的范围之内
@Size(min=15, max=60)
@Email验证是否是合法的邮件地址
@Email
@Past验证Date和Calendar对象是否在当前时间之前
@Past
@Future验证Date和Calendar对象是否在当前时间之后
@FutureDate
@Pattern验证String对象是否符合正则表达式的规则
Pattern(regexp="[1][3,8][3,6,9][0-9]{8}")
Hibernate Validator扩展注解 Hibernate Validator是JSR 303的一个参考实现,除了支持所有标准的校验注解之外,它还扩展了如下表所示的注解.
注解
功能
实例
@URL验证是否是合法的URL
@URL
@CreditCardNumber验证是否是合法的信用卡号码
@CreditCardNumber
@Length(min,max)验证字符串的长度必须在指定的范围内
@Length(min=6, max=8)
@NotEmpty检查元素是否为Null或者 Empty。用于Array,Collection,Map,String
@NotEmpty
@Range(min,max,message)验证属性值必须在合适的范围内
@Range(min=18, max=60, message="学生的年龄必须在18岁到60岁之间")
# 示例 测试JSR 303校验 #
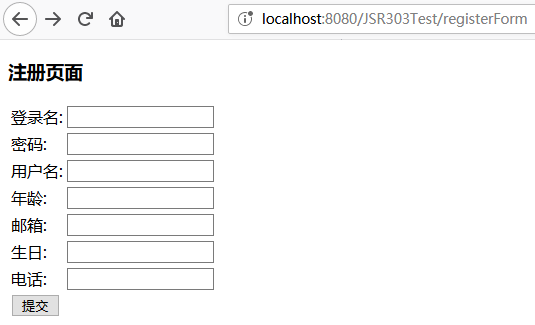
## registerForm.jsp ##
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8" %> <%@taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" > <title>测试JSR 303</title> </head> <body> <h3>注册页面</h3> <!-- 绑定到模型中的user对象 --> <form:form modelAttribute="user" method="post" action="login" > <table> <tr> <td>登录名:</td> <!-- 绑定到模型中user对象的loginname属性 --> <td><form:input path="loginname" /></td> <!-- 当user对象的loginname验证失败时显示 --> <td><form:errors path="loginname" cssStyle="color:red" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>密码:</td> <!-- 绑定到模型中user对象的password属性 --> <td><form:input path="password" /></td> <td><form:errors path="password" cssStyle="color:red" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>用户名:</td> <!-- 绑定到模型中user对象的username属性 --> <td><form:input path="username" /></td> <!-- 当user对象的username验证失败时显示 --> <td><form:errors path="username" cssStyle="color:red" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>年龄:</td> <!-- 绑定到模型中user对象的age属性 --> <td><form:input path="age" /></td> <td><form:errors path="age" cssStyle="color:red" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>邮箱:</td> <!-- 绑定到模型中user对象的email属性 --> <td><form:input path="email" /></td> <!-- 当user对象的email验证失败时显示 --> <td><form:errors path="email" cssStyle="color:red" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>生日:</td> <td><form:input path="birthday" /></td> <td><form:errors path="birthday" cssStyle="color:red" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td>电话:</td> <td><form:input path="phone" /></td> <td><form:errors path="phone" cssStyle="color:red" /></td> </tr> <tr> <td><input type="submit" value="提交" /></td> </tr> </table> </form:form> </body> </html>
registerForm.jsp是一个注册页面,用于提交用户注册信息,注册信息包括用户名、密码、邮箱、电话等。之后将在后台使用JSR 303进行验证。
User.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 public class User implements Serializable private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L ; @NotBlank private String loginname; @NotBlank @Length (min = 6 ,max = 8 ) private String password; @NotBlank private String username; @Range (min = 15 ,max = 60 ) private int age; @Email private String email; @DateTimeFormat (pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd" ) @Past private Date birthday; @Pattern (regexp = "[1][3,8][3,6,9][0-9]{8}" ) private String phone; public User () { super (); } @Override public String toString () { return "User [loginname=" + loginname + ", password=" + password + ", email=" + email + ", username=" + username + ", birthDate=" + birthday + ", phone=" + phone + "]" ; } }
User类使用了Hibernate Validator的注解对前台提交的数据进行验证。
UserController.java 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 @Controller public class UserController @GetMapping (value = "/registerForm" ) public String registerForm (Model model) { User user = new User(); model.addAttribute("user" , user); return "registerForm" ; } @PostMapping (value = "/login" ) public String login (@Valid @ModelAttribute User user, Errors errors, Model model) { System.out.println(user); if (errors.hasErrors()) { return "registerForm" ; } model.addAttribute("user" , user); return "success" ; } }
在UserController中的login方法使用@Valid注解对提交的数据进行校验,后面跟着Errors对象保存校验信息。如果errors中有错误信息,则返回registerForm页面,验证通过则跳转到success页面.
success.jsp 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8" %> <%@ taglib uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt" prefix="fmt" %> <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8" > <title>测试JSR 303</title> </head> <body> <h3>测试JSR 303</h3> <br>登录名:${requestScope.user.loginname } <br> 密码:${requestScope.user.password } <br> 用户名:${requestScope.user.username } <br> 年龄:${requestScope.user.age } <br> 邮箱:${requestScope.user.email } <br> 生日: <fmt:formatDate value="${requestScope.user.birthday}" pattern="yyyy年MM月dd日" /> <br> 电话:${requestScope.user.phone } <br> </body> </html>
由于<mvc:annotation-driven/>会默认装配好一个LocalValidatorFactoryBean,因此springmvc-config.xml配置文件中只是基本配置,不需要增加其他的配置。
国际化错误提示信息 而在实际项目中,我们希望错误信息更加人性化、更具可读性,同时还希望显示国际化的错误信息。接下来我们就为项目加入国际化的错误信息。Spring MVC支持国际化显示数据校验的错误信息。每个属性在数据绑定和数据校验发生错误时,都会生成一个对应的FieldError对象,FieldError对象实现了org.springframework.context.MessageSourceResolvable接口,顾名思义MessageSourceResolvable是可用国际化资源进行解析的对象MessageSourceResolvable接口有如下3个方法:
方法
描述
Object[] getArguments()返回一组参数对象。
String[] getCodes()返回一组消息代码,每一个代码对应一个属性资源,可以使用getArguments()返回的参数对资源属性值进行参数替换。
String getDefaultEessage()默认的消息,如果没有装配相应的国际化资源那么显示的所有错误信息都是默认的.
### 错误消息代码 ###
当一个属性校验失败后,校验框架会为该属性生成4个消息代码,这些代码以校验注解类名为前缀,结合类名、属性名以及属性类型名生成多个对应的消息代码。
例如之前的User类的loginname属性上标注了一个@NotBlank注解,当该属性的值不满足@NotBlank所定义的限制规则时,就会产生以下4种错误代码:
错误代码
描述
NotBlank.user.loginname根据类名、属性名产生的错误代码。
NotBlank.loginname根据属性名产生的错误代码。
NotBlank.java.lang.String根据属性类型产生的错误代码
NotBlank根据验证注解名产生的错误代码。
当使用 Spring MVC标签显示错误信息时, Spring MVC会查看Web上下文是否装配了对应的国际化消息,如果没有,则显示默认的错误消息,否则使用国际化消息对错误代码进行显示。
知道错误对象的错误码是对应国际化消息的键名称后,接下来就非常简单了,定义两个国际化资源文件,在国际化资源文件中为错误代码定义相应的本地化消息内容 。
message_en_US.properties 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 NotBlank.user.loginname= Loginname is not null NotBlank.user.password= Password is not null Length.user.password=Password length must be between 6 and 8 NotBlank.user.username= Username is not null Range.user.age=Age must be between the ages of 15 to 60 Email.user.email=Must be a legitimate email address Past.user.birthday=Birthday must be a date in the past Pattern.user.phone=Invalid phone number
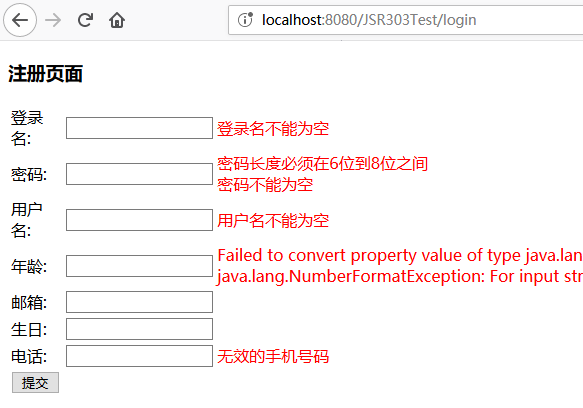
message_zh_CN.properties 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 NotBlank.user.loginname=登录名不能为空 NotBlank.user.password=密码不能为空 Length.user.password=密码长度必须在6 位到8 位之间 NotBlank.user.username=用户名不能为空 Range.user.age=年龄必须在15 到60 岁之间 Email.user.email=必须是合法的邮箱地址 Past.user.birthday=生日必须是一个过去的日期 Pattern.user.phone=无效的手机号码
接下来还需要在springmvc-config.xml配置文件中增加国际化的配置,如下所示:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 <bean id ="messageSource" class ="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource" > <property name ="basenames" value ="message" /> </bean >
springmvc-config.xml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi ="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:mvc ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:p ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" xsi:schemaLocation ="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.3.xsd" > <context:component-scan base-package ="org.fkit" /> <mvc:annotation-driven /> <mvc:default-servlet-handler /> <bean id ="viewResolver" class ="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver" p:prefix ="/WEB-INF/content/" p:suffix =".jsp" /> <bean id ="messageSource" class ="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource" > <property name ="basenames" value ="message" /> </bean > </beans >
测试 乱填表单
错误提示
原文链接: 6.4 数据校验 6.4.2 JSR 303校验