9.5 示例3:下载计数Filter
本例子中,下载计数Filter将会示范如何在Filter中计算资源下载的次数。这个示例特别有用,它将会得到文档、音频文件的受欢迎程度。作为简单的示例,这里将数值保存在属性文件中,而不保存在数据库中。其中资源的ULR路径将作为属性名保存在属性文件中。
因为我们把值保存在属性文件中,并且Filter可以被多线程访问,因此涉及线程安全问题。用户访问一个资源时,Filter需要读取相应的属性值加1,然后保存该值。如果第二个用户在第一个线程完成前同时访问该资源,将会发生什么呢?计算值出错。在本例中,读写的同步锁并不是一个好的解决这个问题的方法,因为它会导致扩展性问题。
本示例中,解决这个线程安全问题是通过Queue以及Executor。如果不熟悉这两个Java类型的话,请看第18章”多线程及线程安全”
简而言之,进来的Request请求将会保存在单线程Executor的队列中。替换这个任务十分方便,因为这是一个异步的方法,因此你不需要等待该任务结束。Executor一次从队列中获取一个对象,然后做相应属性值的增加。由于Executor只在一个线程中使用,因此可以消除多个线程同时访问一个属性文件的影响。
DownloadCounterFilter.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
| package filter;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import javax.servlet.Filter;
import javax.servlet.FilterChain;
import javax.servlet.FilterConfig;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.ServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.ServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebFilter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@WebFilter(
filterName = "DownloadCounterFilter",
urlPatterns={"/*"}
)
public class DownloadCounterFilter
implements
Filter
{
ExecutorService executorService =
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
Properties downloadLog;
File logFile;
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig)
throws ServletException
{
System.out.println("DownloadCounterFilter");
String appPath =
filterConfig
.getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/");
logFile = new File(appPath, "downloadLog.txt");
if(!logFile.exists()) {
try {
logFile.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
downloadLog = new Properties();
try {
downloadLog
.load(new FileReader(logFile));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void destroy()
{
if(logFile.exists())
{
logFile.delete();
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request,
ServletResponse response, FilterChain filterChain)
throws IOException, ServletException
{
HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest =
(HttpServletRequest) request;
final String uri = httpServletRequest.getRequestURI();
executorService.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String property = downloadLog.getProperty(uri);
if (property == null) {
downloadLog.setProperty(uri, "1");
} else {
int count = 0;
try {
count = Integer.parseInt(property);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
}
count++;
downloadLog.setProperty(uri,
Integer.toString(count));
}
try {
downloadLog
.store(new FileWriter(logFile), "");
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
});
filterChain.doFilter(request, response);
}
}
|
代码详解
init方法
如果在当前应用的工作目录中不存在downloadLog.txt文件,这个Filter的init方法就会创建它:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
String appPath =
filterConfig
.getServletContext()
.getRealPath("/");
logFile = new File(appPath, "downloadLog.txt");
if(!logFile.exists()) {
try {
logFile.createNewFile();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
|
接着创建Properties对象,并读取该文件:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
downloadLog = new Properties();
try {
downloadLog.load(new FileReader(logFile));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
|
注意,Filter的实现类中引用到了ExecutorService(Executor的子类):
1
2
| ExecutorService executorService =
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
|
destroy方法
且当Filter销毁时,会调用ExecutorService的shutdown方法:
1
2
3
| public void destroy() {
executorService.shutdown();
}
|
doFilter方法
Filter的doFilter实现中大量地使用到这个Job。每次URL请求都会调用到ExecutorService的execute方法,然后才调用FilterChaing.doFilter()。该任务的execute实现非常好理解:它将URL作为一个属性名,从Properties实例中获取该属性的值,然后加1,并调用flush方法写回到指定的日志文件中:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| public void run() {
String property = downloadLog.getProperty(uri);
if (property == null) {
downloadLog.setProperty(uri, "1");
} else {
int count = 0;
try {
count = Integer.parseInt(property);
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
}
count++;
downloadLog.setProperty(uri,
Integer.toString(count));
}
try {
downloadLog
.store(new FileWriter(logFile), "");
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
|
这个Filter的urlPatterns设置为*,即过滤所有URL,实际应用中可以修改为过滤某些特定的文件,如:只过滤pdf文件
运行效果
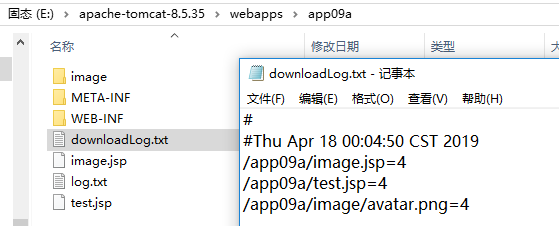
访问项目中的多个jsp页面,然后多刷新几次,然后打开打开downloadLog.txt文件(在Tomcat中的路径E:\apache-tomcat-8.5.35\webapps\app09a\downloadLog.txt)可以看到效果,如下图所示:
原文链接: 9.5 示例3:下载计数Filter
